Ethylene glycol, a popular industrial chemical used in the manufacture of polyester fibers and in industrial applications like antifreeze, has the structure shown below:
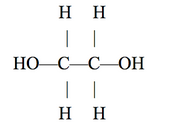
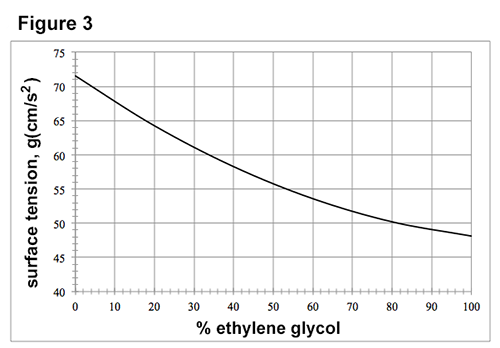
Figures 1-3 each show how a property of solutions of ethylene glycol in H2O varies as the concentration of ethylene glycol increases at 1 atmosphere (atm) of pressure. Concentration is given as the percent ethylene glycol by mass in H2O. Figure 1 shows how the freezing point varies with % ethylene glycol. Figure 2 shows how the boiling point varies with % ethylene glycol. The surface tension is the property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force due to the cohesive forces between molecules in the liquid. Figure 3 shows how surface tension varies with % ethylene glycol at 25°C.


Passage data adapted from http://www.meglobal.biz/media/product_guides/MEGlobal_MEG.pdf.